Blog
What is an Interlocking Nail Implant and How Does It Work?
The use of an Interlocking nail implant has transformed the field of orthopedic surgery. This device provides stability to long bone fractures. Reports indicate a success rate exceeding 90% in certain cases. Surgeons often prefer it for its minimally invasive nature. These implants allow for quicker recovery times, reducing hospital stays significantly.
However, the implementation of interlocking nail implants is not without challenges. Complications such as infection or improper alignment occur in a small percentage of cases. A study noted that around 5% of procedures resulted in need for revision surgery. Awareness of these risks is essential for both patients and medical professionals.
Interlocking nail implants continue to evolve. Innovations in materials and design may further improve outcomes. Yet, the emphasis on rigorous training remains crucial. Surgeons must carefully evaluate individual cases to optimize treatment. The journey of healing with an interlocking nail implant is complex but holds great promise.
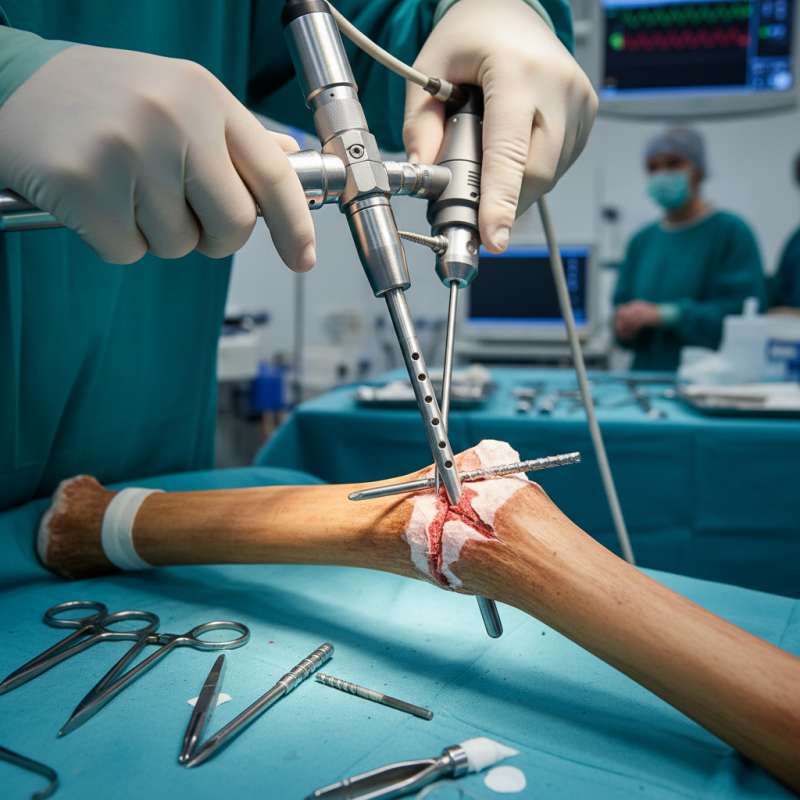
Definition of Interlocking Nail Implant and Its Purpose
An interlocking nail implant is a specialized device used in orthopedic surgeries. It is primarily designed for the stabilization of fractures, especially in long bones like the femur and tibia. This implant plays a crucial role in enhancing the healing process. It allows for precise alignment and support during recovery. Surgeons insert the nail through the bone and secure it in place using locking screws.
The purpose of an interlocking nail implant extends beyond mere stabilization. It facilitates weight-bearing earlier compared to traditional casting methods. As patients regain mobility sooner, it can lead to a more active recovery. However, not all cases are straightforward. There can be complications, such as infection or improper alignment. These factors necessitate careful planning and consideration prior to surgery.
Using an interlocking nail is not without its challenges. Every patient's anatomy differs, which can complicate the implantation process. It requires skilled hands and experience to navigate these variations. Surgeries may not always yield immediate results. Healing can be a slow journey, demanding patience and perseverance from patients. In the end, the goal is to return to a normal life, but the pathway may have bumps along the way.
Interlocking Nail Implant Usage in Orthopedic Surgery
This bar chart illustrates the usage of interlocking nail implants in various orthopedic surgeries over the past year. The data reflects the percentage of surgeries performed using interlocking nail implants for different types of fractures.
Components and Design Features of Interlocking Nail Implants
Interlocking nail implants are innovative devices used in orthopedic surgery, particularly for the stabilization of fractures in long bones. These implants consist of a long, metal rod that is inserted into the medullary cavity of a bone. The primary components include the nail itself, locking screws, and an insertion tool. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and alignment of the fractured bone.
The design features of interlocking nails are vital for their performance. Many implants are made from titanium or stainless steel, which provide strength and biocompatibility. The locking screws create a dynamic system, allowing the nail to resist axial and rotational forces. Data from recent clinical reports indicate that interlocking nails can reduce healing time by approximately 30%. However, the technique requires precise placement. Improperly positioned screws can lead to complications, including nonunion or malalignment of the fracture, necessitating further surgical intervention.
Surgeons often face challenges in determining the appropriate nail length and diameter based on the patient's anatomy. This variability can affect the overall success of the procedure. Additionally, it's crucial to evaluate the patient's bone quality before surgery. Older adults or those with osteoporosis may present unique difficulties. Despite these challenges, the advantages of interlocking nails in facilitating bone healing remain significant.
Mechanism of Action: How Interlocking Nails Stabilize Fractures
Interlocking nails are a type of implant used in orthopedic surgery. They are designed to stabilize fractured bones. These implants provide internal support when healing from complex fractures. They work by aligning the fractured bone pieces. This alignment is crucial for effective healing.
The mechanism of action involves inserting long, metal rods into the bone. Surgeons pass these rods through the center of the bone and secure them at both ends with locking screws. This structure creates a stable frame around the fracture. The interlocking mechanism prevents movement at the fracture site, which is vital during recovery.
However, selecting this method isn’t always straightforward. Sometimes, interlocking nails may lead to complications. For instance, they can cause discomfort or interfere with adjacent tissues. It’s essential to carefully assess each case. Not every fracture will benefit equally from this technique. Balancing benefits and risks is crucial for successful outcomes.
Procedural Steps for Inserting an Interlocking Nail Implant
Inserting an interlocking nail implant is a detailed process. Before starting, the patient is usually placed under anesthesia to ensure comfort. The surgical site is carefully prepared and draped. The surgeon then makes an incision on the skin over the bone that needs stabilization.
X-ray imaging may guide the process. After exposing the bone, the surgeon carefully drills a hole into it. This is where the nail will be inserted. The nail is designed to lock into place, providing stability. The next step involves ensuring the implant aligns correctly with the bone. The locking screws are then inserted through the holes in the nail. This step requires precision to avoid any misalignment.
After securing the implant, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures. However, complications may arise, such as misplacement of screws or inadequate healing. Surgeons must reassess their technique to avoid these issues. Rehabilitation is essential afterward, allowing the patient to gradually regain strength and function. Each step in this process holds significance, and attention to detail is crucial for successful outcomes.
Benefits and Risks Associated with Interlocking Nail Implant Surgery
Interlocking nail implants are increasingly popular in orthopedic surgeries. They are often used to treat bone fractures, particularly in long bones. This method offers stability and encourages proper healing. However, surgery comes with several benefits and risks.
One significant benefit is the stable fixation of fractured bones. This is crucial for effective recovery. It allows patients to regain mobility faster. Interlocking nails can be adjusted to the specific needs of the patient. They can accommodate various fracture types and locations. Despite these advantages, risks exist. Possible complications include infection, improper alignment, or hardware failure.
Patients should weigh these risks carefully. Some might experience prolonged pain or limited movement post-surgery. It's vital to consult with healthcare providers to discuss individual circumstances. Each case is unique, and outcomes can vary. Understanding both sides is essential for informed decision-making regarding interlocking nail implants.